Principle: Archimedes method, ,
, and
and are the system of heavy hammer and immersed melt filament respectively,
are the system of heavy hammer and immersed melt filament respectively, is the acceleration of gravity,
is the acceleration of gravity, is the additional force caused by the surface tension of the melt, generally,
is the additional force caused by the surface tension of the melt, generally,  ,
, is the radius of the hanging wire,
is the radius of the hanging wire, is the surface tension of the melt, and
is the surface tension of the melt, and is the wetting angle between the melt and the filament.
is the wetting angle between the melt and the filament.
Advantages: considering the influence of volume expansion and surface tension, the test accuracy is greatly improved, with an accuracy of 0.5%.
Scope of application: stable without volatilization, low viscosity, uniform in liquid state, no precipitation, such as various molten salts and some liquid metals.
Schematic diagram of device principle:

Aid diagram
Result:

NCl experiment result and literature result comparison
Principle: CVCC method, that is, continuously changing conductance cell, that is, changing the length of the capillary conductance cell at a fixed external frequency, and then reading out the total impedance of the circuit at different conductance cell lengths. ,
, is the molten salt resistance,
is the molten salt resistance, is the length of the conductivity cell,
is the length of the conductivity cell, is the cross-sectional area of the conductivity cell,
is the cross-sectional area of the conductivity cell, is the constant of the conductivity cell,
is the constant of the conductivity cell,  is the conductivity.
is the conductivity.
Advantages: during calibration and measurement, the consistency requirements of the conductivity cell are no longer as strict as those of the fixed conductivity cell constant method, which facilitates the test. The measurement accuracy is 5%, and the reproducibility is 3%.
Scope of application: stable without volatilization, low viscosity, uniform in liquid state, no precipitation, such as various molten salts and some liquid metals.
Principle: step cooling curve method
Measurement accuracy:±1℃
Historical data: sodium chloride step cooling curve
Schematic diagram of device principle:

Crystal temperature measurement aid diagram
Result:

5.1 Rotational method
Principle: rotation method, ,
, is the moment generated by rotation,
is the moment generated by rotation, and
and is the radius of the inner and outer cylinders respectively,
is the radius of the inner and outer cylinders respectively,  is the depth of the inner cylinder immersed in the liquid,
is the depth of the inner cylinder immersed in the liquid, is the angular velocity of rotation,
is the angular velocity of rotation, is the additional pipe length introduced by the end effect caused by the viscous resistance of the end face of the inner cylinder.
is the additional pipe length introduced by the end effect caused by the viscous resistance of the end face of the inner cylinder.
Advantages: the double hanging wire software connection technology realizes the measurement of the viscosity of high-temperature liquid molten salt for the first time, filling the gap in the field of high-temperature and low viscosity measurement.
Viscosity test range:1.6-20cp(low viscosity),50-105 cp (vacuum high viscosity)
Measurement accuracy:<0.2cp
Schematic diagram of device principle:

Sample(oil) result:

5.2 Torsion cylinder method
Principle: oscillating cup, by rotating and vibrating the sample liquid in the container, internal friction will occur between liquid molecules. The logarithmic decay rate of rotation is measured, and the viscosity data is obtained according to the relationship between the logarithmic decay rate and viscosity.
Advantages: suitable for the measurement of high temperature and low viscosity liquid samples, especially low viscosity samples such as metals / alloys.
Schematic diagram of device principle:

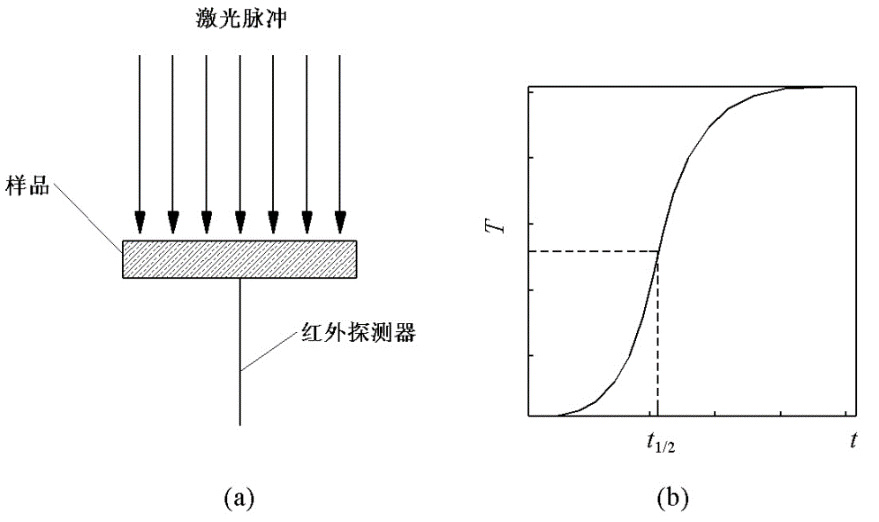
Principle: laser flash method, based on Park formula, ,where
,where and
and and
and are the thermal diffusion coefficient of the sample, the thickness of the sample and 1 / 2 of the time when the temperature of the laser pulse emitted to the lower surface rises to steady state, respectively.
are the thermal diffusion coefficient of the sample, the thickness of the sample and 1 / 2 of the time when the temperature of the laser pulse emitted to the lower surface rises to steady state, respectively.
Application: isotropic solid samples.
Schematic diagram of device principle:
Method: Short hot wire method
Testing range: molten salt
Schematic diagram of device principle:

 浙公网安备33018302001591号ICP备案编号:浙ICP备2022013385号-2
浙公网安备33018302001591号ICP备案编号:浙ICP备2022013385号-2